FREE Online Courses: Knowledge Awaits – Click for Free Access!
Network Topology is the arrangement in which we can connect computer systems or network devices. Topologies define both the physical and logical aspects of a network. In the same network, the logical and physical topologies could be the same or distinct.
What is Network Topology?
Network topology is the physical or logical arrangement of a network’s nodes, devices, and connections. If a network is a city then the topology is the road map.
There are several methods to arrange and manage a network, just as there are numerous ways to arrange and maintain a city.
Each has pros and cons and depending on the needs, various arrangements might provide a higher level of connectivity and security.
Network topologies are broadly defined within 2 categories:
a. Physical – The physical network topology refers to the real connections (wires, cables, and so on) that make up how the network is set up.
b. Logical – This is a higher-level concept of how the network is configured, including which nodes link to each other and in what manner, as well as how data is transported over the network.
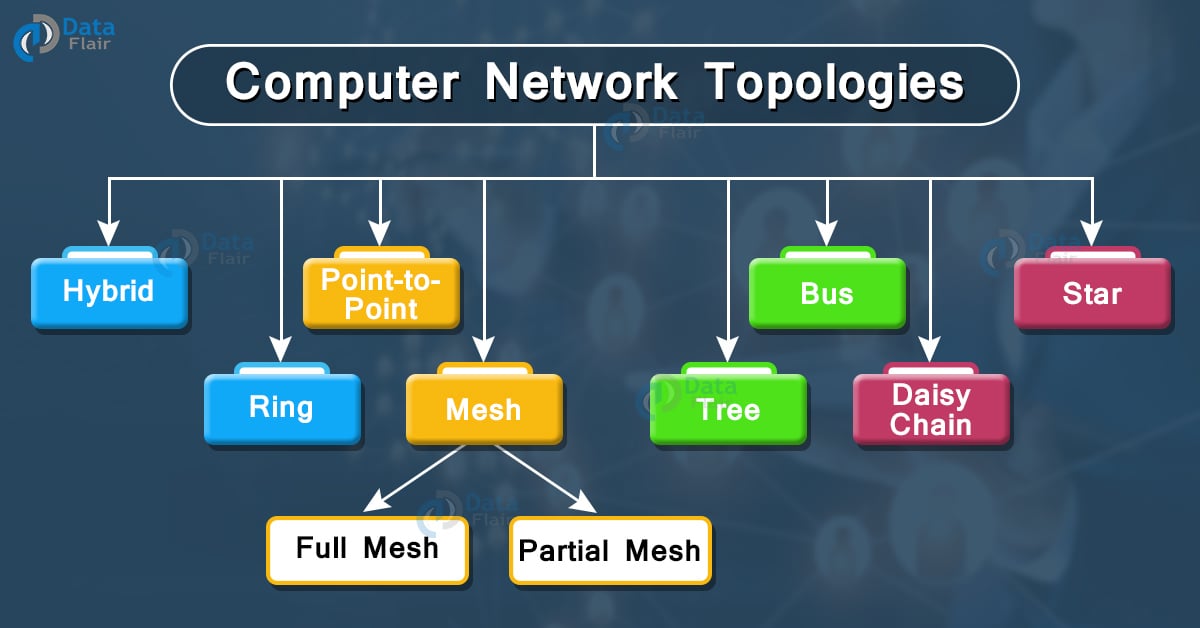
Types of Network Topologies:
1. Point-to-Point networks:
Point-to-Point networks have exactly 2 hosts, where the receiving end of one host connects directly to the sending end of the other host or vice-versa. This is usually done with the help of a single, long cable that connects the two hosts (the hosts may be routers, servers, PCs etc.).
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
The connections between the 2 hosts may be logical too, where there may be multiple other devices connected in between the 2 hosts, but the hosts are unaware of this and see the network as if they are connected directly to each other.
Advantages of point to point topology:
- Very high bandwidth and speed because of only 2 end devices sharing the link.
- Low latency connection.
- Replacement of nodes is easy, as there are only 2 of them.
- Easy to set up and maintain.
Disadvantages of point to point topology:
- Not feasible for nodes spread out over large distances.
- In case of damage to the common link, the whole network will go down.
- If any of the 2 nodes stops working, it interrupts data transfer across the network.
2. Bus Topology:
In this topology, all the devices share a common communication channel, and there may be multiple devices connected across this common link. We can define one of the hosts as the ‘Bus Master’.
Both the ends of the shared channel have a ‘terminator’. Transfer of data is unidirectional, and as soon as any data reaches the terminator, it is removed from the common link.
Advantages of bus topology:
- In case any node fails, it does not affect the operation of the network.
- It is easy to connect/disconnect devices from the network without interrupting the operation of the network.
- Expanding the network just requires joining more lengths of cable together.
- Bus topology is a well-known technology since the installation and troubleshooting procedures are widely understood, and hardware components are readily available.
Disadvantages of bus topology:
- If the common link fails, the whole network fails.
- Too many devices may cause the network to slow down.
- It is difficult to find the exact fault when something fails.
- Only one device can transmit at a time.
- Signals will bounce back if terminators are not configured correctly.
- Signal interference occurs when two nodes send messages at the same time, causing their signals to collide.
- Attenuation is a signal loss that causes communication problems. To regenerate the signal, repeaters have to be used.
- Furthermore, data is “half-duplex,” which means it cannot be transmitted in two opposing directions at the same time, making this structure unsuitable for high-traffic networks.
3. Star Topology:
All devices in the network are directly connected to one central device, known as the hub device (thus, there is a point to point connection between each device and the hub).
The central device can be a hub, switch, or a router. All communication between the different devices in the network has to pass through the hub device.
Advantages of Star Topology:
- High speed data transfer
- Easy to add more devices, just a single cable is required.
- Network management is easy due to the presence of the hub device.
- Easy to add/remove devices without affecting operation of the network.
- Easy to locate problems in the network.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
- If the hub fails, the entire network fails.
- Requires more wires compared to bus and ring topologies.
- The overall bandwidth and performance of the network are also restricted by the settings and technical specifications of the central node, making star topologies costly to set up and operate.
4. Ring Topology:
Each host machine in a ring topology links to exactly two other machines, forming a circular network structure. When a host tries to communicate with or send a message to a host that isn’t directly adjacent to it, the data is routed through all the hosts in between.
The communication in a ring topology may be unidirectional or bidirectional.
Token passing is the most popular ring topology access mechanism. A token is a frame that circulates throughout the network. Token passing is a network access mechanism that involves passing a token from one node to another.
Working of Token Passing:
- A token travels across the network, passing from computer to computer until it reaches its destination.
- The sender changes the token by including the address in addition to the contents.
- The data is transferred from one device to the next until the target address is found to match. When the destination device receives the token, it sends an acknowledgment to the sender.
- A token serves as a carrier in a ring topology.
Dual Ring Topology:
Half-duplex means data may only travel in one way at a time in a network with ring architecture. It is possible to make ring topologies full-duplex by adding a second link between network nodes.
Advantages of Dual Ring Topology:
- Each node contains two connections on either side, allowing information to be transmitted in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions along the network.
- Due to the redundant nature and backup capabilities of a dual-ring topology, many of the drawbacks of classic ring topology may be overcome.
- If one ring breaks within a node, the other ring can continue to transfer data, providing an extra layer of protection.
Advantages of Ring Topology:
- Better performance than bus topology, even with more devices.
- Maintenance is easier.
- Chances of data collision are less.
- Can handle a higher number of nodes than bus topology.
- Troubleshooting is easier due to easier identification of faults in cables.
- Ring topology is cheaper compared to mesh, hybrid and tree topologies.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:
- If one cable has a fault, the whole ring is interrupted, which means an interruption in the network.
- Data must pass through multiple devices, which may be a security concern.
- In order to reconfigure, add, or delete nodes, we must take the entire network offline.
- Because all network devices share bandwidth in a ring architecture, the addition of new devices can contribute to increased communication latency.
- To avoid overburdening the network’s resources and capabilities, network managers must be careful of the devices introduced to the topology.
5. Mesh Topology:
A host is connected to one or more hosts in this form of network topology. Hosts may be connected directly to all other hosts, or hosts may be connected directly to only a few other hosts. The connection between the hosts is point-to-point. Number of cables required to set up a mesh topology is: (n*(n-1))/2
There are 2 types of mesh topologies:
- Full mesh: All hosts are connected to all other hosts in the network using a point-to-point connection.
- Partial Mesh: Not all hosts are connected to other hosts with a point-to-point connection, the connections are made purely based on the network requirements.
Advantages of Mesh Topology:
- Reduction in congestion as there are special point-to-point links between devices.
- Provides multiple routes for data transfer
- Easier to identify faults due to the presence of point-to-point links.
- Provides a high level of privacy and security.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:
- Requires a lot of cables and data transfer ports to set up.
- More expensive as compared to bus, star, ring etc.
- Difficult to install due to the presence of a large number of links.
- The number of redundant connections in this architecture is significant, reducing network efficiency.
- Mesh topology networks are massive and challenging to maintain. If the network is not closely monitored, a communication connection breakdown will go undetected.
6. Tree Topology:
Most commonly occurring form of network topology, which uses the properties of both star and bus topology. Tree topology is organized into different levels, namely:
- Access Layer: Lowest layer, involves computers.
- Distribution Layer: Middle layers, joins and coordinates the upper and lower layers.
- Core Layer: Highest layer, also the central part of the network.
Advantages of Tree Topology:
- Easy to scale, as more computers can be added easily into the access layer.
- In case of damage to a node, it does not affect other nodes in the network.
- Easy to identify faults and maintain the network.
- Easy to set up, because point-to-point links are used for individual segments.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology:
- Tree topologies are costly due to the massive quantity of cable required to link each item inside the hierarchical architecture.
- If the core layer fails, the entire network fails.
- Because of the network’s hierarchical complexity and linear structure, adding additional nodes to a tree topology may soon become an unmanageable, not to mention costly, experience.
7. Daisy Chain:
This topology connects all hosts in a straight line. Except for the end hosts, all hosts are connected to only two other hosts. It is similar to a ring topology where the ring has been disconnected at a node.
Advantages of Daisy Chain:
- Easy to set up and maintain.
- Easier fault identification.
- Cheaper because only one piece of cable connects 2 devices.
Disadvantages of Daisy Chain:
- Every link is a potential point of failure.
- If a link fails, the network divides itself into 2 smaller networks.
- Security concerns due to data passing through multiple devices before reaching its destination.
8. Hybrid Topology:
When we combine different topologies together in order to form a larger network, we can call it a hybrid topology. The resulting network will have all the advantages and disadvantages of the constituent topologies.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Combines the good qualities of various topologies.
- Very scalable and reliable
- Easy to change as per the requirement of the network.
- Hybrid topology is extremely successful because we can customise it so that we increase or amplify the strengths and make the weaknesses less prominent.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology:
- Expensive due to the larger number of cables and ports required.
- The design of the Hybrid network is the main disadvantage of the Hybrid architecture. The architecture of the Hybrid network is extremely complex to build.
- The Hubs used in the Hybrid topology are highly costly since they are not like the Hubs used in other topologies.
Network Topology Software:
- It is critical to first establish a complete understanding of the network’s functionality before choosing how to build network architecture that is perfect for the purposes and use requirements of a network.
- Network topology mapper software is a useful network topology tool that generates network topology diagrams.
- Network topology mapping software depicts how devices link and assists in determining the most effective topology.
- Once a configuration is chosen, network topology design software, network configuration management tools, and network management software solutions assist not only in network topology construction, but also in automating configuration, continuously monitoring performance, and troubleshooting network issues.
- In the market, there are both proprietary and free network topology software options, such as Microsoft Visio and LibreOffice Draw.
How to Map Network Topology?
Topology diagrams are useful when first designing a network. They let you observe how the information will travel throughout the network, allowing you to forecast possible bottlenecks. Visual representation facilitates the creation of a streamlined and efficient network architecture while also serving as a useful reference point for troubleshooting problems.
A topology diagram is also required for a thorough knowledge of your network’s operation. A topology diagram, in addition to aiding with troubleshooting, may help you visually determine which parts of equipment your network lacks, or which nodes require monitoring, updating, or replacement.
Why Is Network Topology Important?
- The design of a network is critical for numerous reasons. Above all, it is critical in determining how successfully a network operates.
- Choosing the proper topology may boost performance while making it simpler to detect problems, fix mistakes, and distribute resources more efficiently throughout the network to guarantee optimal network health.
- A simplified and well-managed network architecture may improve energy and data efficiency, lowering operating and maintenance expenses.
A network topology diagram is often used to display and alter the architecture and structure of a network. These diagrams are important for a number of reasons, the most important of which is that they give visual representations of both physical and logical layouts, allowing administrators to understand the links between devices while troubleshooting.
A network’s layout has a direct influence on network functionality. The appropriate topology may enhance performance and data efficiency, optimise resource allocation, and save operating costs.
One of the most common applications of network topology is to specify the design of various telecommunication networks, such as computer networks, command and control radio networks, etc.
What Tools Help Manage and Monitor Networks?
On the market, there are a few network topology mapping products.
One of the most popular tools is Microsoft Visio, which allows the construction of a network by adding various nodes and devices on a canvas-like interface. While this works well for smaller networks, drawing each new node becomes cumbersome when dealing with a large number of devices and topologies distributed throughout an entire organization.
Other choices, such as Lucidchart and LibreOffice Draw, are either free or provide free trials, and although they are viable options, especially if money is an issue, they do not have a full range of premium network mapping capabilities to make network management easier and less time-consuming.
The use-cases for network managing and monitoring tools can be:
1. Network Configuration:
- As an organization or network expands, the network architecture may become more layered or complicated, making it more difficult to deploy settings with confidence throughout the whole network.
- The complex network topology, on the other hand, is no problem for configuration management systems: software can generally auto-detect each node on the network, allowing conventional configurations to be deployed or flagging any configurations that are not expected.
- Network configuration management software can also identify vulnerabilities, allowing anybody to fix them and make a network more secure.
- Finally, these technologies indicate the lifetime of the devices on a network, notifying users when devices reach their end-of-service or end-of-life points, allowing them to replace them before issues emerge.
2. Network Performance Troubleshooting:
- Using network management software is a good way to monitor overall performance.
- A performance manager can monitor network problems, outages, and performance concerns.
- A performance management tool will also have the capability of establishing network performance baselines and establishing a clear image of how a network normally acts when healthy.
- Then, by establishing alerts for when a network behaves unexpectedly or outside of these baselines, one may rapidly monitor, diagnose, and fix issues.
Which Topology Is Best For Your Network?
Because no network topology is perfect or better than the others, selecting the best structure for your organisation will be determined by the demands and size of your network. The most important factors to consider are:
1. Cable Length:
In general, the more wire in network architecture, the more labor it will take to set up. Bus and star topologies are on the lighter side of things, being relatively lightweight, whereas mesh networks are significantly more cable- and labor-intensive.
2. Cable Type
Both coaxial and twisted-pair cables employ insulated copper or copper-based wire, whereas the construction of fiber-optic cables involves thin and flexible plastic or glass tubes. Twisted-pair cables are less expensive than coaxial cables but have less bandwidth.
Fiber-optic cables are more efficient and can carry data much quicker than twisted-pair or coaxial cables, but they are also more expensive to install since they require extra components such as optical receivers.
As with network topology, the wiring you choose is determined by the demands of your network, such as the applications you’ll be running, the transmission distance, and desired performance.
3. Cost:
Complex network topologies will take more time and money to set up, for example, when linking a more sophisticated network structure with more expensive cables.
Determining the best topology for your purposes, then, is a matter of striking the proper balance between installation and running expenses and the amount of network performance you require.
4. Scalability:
Star topologies are popular because they allow for the addition, removal, and modification of nodes while causing minimum disturbance to the rest of the network. Modifying ring networks is only possible when the network is offline.
Summary
This was a concise look at all of the network topologies which are in use today, as well the advantages and disadvantages of each. While some topologies are cheaper and easier to set up, others are expensive and complicated but provide a greater performance advantage over all other topologies.