FREE Online Courses: Click for Success, Learn for Free - Start Now!
Multiplexing is a method of combining and transmitting several data streams across a single media. It is the process of merging data streams, and the gear used for multiplexing is known as a multiplexer.
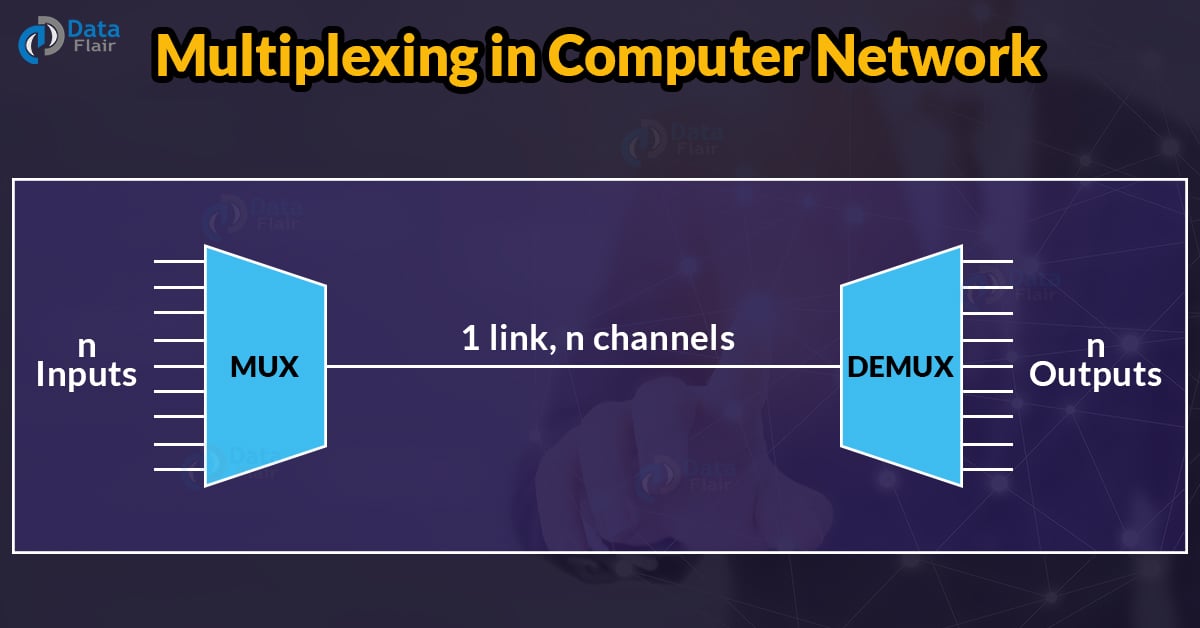
Multiplexing is accomplished by utilising a device known as a Multiplexer (MUX), which combines n input lines to produce a single output line. Multiplexing is done in a many-to-one fashion, with n input lines and one output line.
Demultiplexing is accomplished at the receiving end by employing a device known as a Demultiplexer (DEMUX). DEMUX divides a signal into its constituent components (one input and n outputs). As a result, demultiplexing follows the one-to-many technique.
History of Multiplexing:
- Multiplexing is a method commonly used in telecommunications that allows several phone calls to be transmitted over a single cable.
- Multiplexing was invented in the early 1870s in telegraphy and is now widely used in communication.
- In 1910, George Owen Squier invented telephone network carrier multiplexing.
Need for Multiplexing:
- The signal is sent from sender to receiver via the transmission medium. There can only be one signal on the medium at any given moment.
- If several signals must share a single media, the medium must be split so that each signal receives a fraction of the available bandwidth.
- When numerous signals use the same medium, there is a chance that they will collide. To avoid such collisions, the concept of multiplexing is utilised.
- Transmission services are exorbitantly priced.
Concept of Multiplexing:
- The ‘n’ input lines are routed via a multiplexer, which combines the signals to create a composite signal.
- The composite signal is routed to a Demultiplexer, which divides a signal into component signals and routes them to their appropriate destinations.
Classification of Multiplexing Techniques:
1. Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM):
- It is an analog method.
- Frequency Division Multiplexing is a method that divides the available bandwidth of a single transmission medium into several channels.
- Modulation methods are used to convert the input signals into frequency bands, which are then merged by a multiplexer to produce a composite signal.
- The primary goal of FDM is to divide available bandwidth into multiple frequency channels and assign them to various devices.
- The modulation process divides the input signals into frequency bands, which are subsequently merged to produce a composite signal.
- Sub-carriers are the carriers that are utilised to modulate the signals. They are denoted as f1,f2,…fn.
- Guard bands divide the channels. A guard band is a frequency that neither channel uses.
Applications of FDM
- FDM is widely used in television networks.
- It’s utilised in FM and AM radio broadcasts. Each FM radio station broadcasts at a distinct frequency, which is multiplexed to produce a composite signal. The multiplexed signal is broadcast over the air.
Advantages of FDM:
- For analogue signals, FDM is utilised.
- The FDM modulation technique is relatively basic and straightforward.
- An FDM may send a large number of signals at the same time.
- It does not need any sort of synchronisation between the transmitter and the recipient.
Disadvantages of FDM:
- When low-speed channels are required, the FDM method is employed.
- It has an issue of crosstalk.
- This is necessary to use a large number of modulators.
- It needs a channel with a high bandwidth.
2. Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM):
- Wavelength Division Multiplexing is similar to Frequency Division Multiplexing except for the fact that optical signals are delivered over fibre optic cable.
- WDM is a technique used in fibre optics to enhance the capacity of a single fibre.
- It is utilised to take advantage of the high data rate capabilities of fibre optic cable.
- It is a technique for analogue multiplexing.
- With the aid of a multiplexer, optical signals from several sources are merged to produce a broader spectrum of light.
- The signals are separated at the receiving end by a demultiplexer before being sent to their respective destinations.
- A prism can be used to do multiplexing and demultiplexing.
- Prism can function as a multiplexer by mixing several optical signals to produce a composite signal, which is then sent through a fibre optical connection.
- Prism also does a reverse process, which is signal demultiplexing.
- Dense wavelength division multiplexing merges a large number of channels (30, 40, 50, or more) onto a single fibre. DWDM channels have a very high capacity that is constantly improving.
- Only a few wavelengths are combined using coarse wavelength division multiplexing. This has more widely spread channels and is a less expensive variant of DWDM.
Advantages of WDM:
- Full-duplex transmission is achievable with the aid of WDM.
- WDM is simple to reconfigure.
- With the aid of WDM, several signals may be sent at the same time.
- This method is less costly, and system expansion is simple.
- This method is highly secure.
- Because optical fibre is used in WDM, optical components are more dependable and provide more bandwidth.
Disadvantages of WDM:
- Because optical equipment is used, the cost rises.
- Because of poor bandwidth use, wavelength adjustment might be challenging.
- This technique’s major issue is scalability.
3. Time Division Multiplexing (TDM):
- It is a digital method.
- In the case of Frequency Division Multiplexing, all signals operate at the same time but at various frequencies, whereas in the case of Time Division Multiplexing, all signals operate at the same frequency but at different times.
- The total time available in the channel is divided among multiple users using the Time Division Multiplexing method. As a result, each user is assigned a unique time interval known as a Time slot during which data is to be delivered by the sender.
- For a set period of time, a user assumes control of the channel.
- Data is not sent concurrently in the Time Division Multiplexing method, but rather one at a time.
- The signal is sent in the form of frames in TDM. Frames include a cycle of time slots, with one or more slots allotted to each user in each frame.
- It can multiplex both digital and analogue signals, although it is most commonly used to multiplex digital signals.
Types of Time Division Multiplexing (TDM):
a. Synchronous TDM:
- Synchronous TDM is a method in which each device is allocated a time slot.
- In Synchronous TDM, each device is assigned a time slot regardless of whether the device carries data or not.
- If the device has no data, the slot will stay vacant.
- Signals are transmitted in the form of frames in Synchronous TDM. Frames are used to organise time periods. If a device does not have data for a specific time slot, the empty slot is sent.
- T-1 multiplexing, ISDN multiplexing, and SONET multiplexing are the most common types of Synchronous TDM.
- There are n slots if there are n devices.
Advantages of synchronous TDM:
- This approach is simple to use.
- Using this approach ensures a high level of performance.
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
Disadvantages of Synchronous TDM:
- If a user has no data to send, time slots will be wasted.
- The capacity of the transmission connection must always be greater than the total capacity of the input lines in this multiplexing.
b. Asynchronous TDM:
- Asynchronous TDM is sometimes referred to as Statistical TDM.
- This is a method in which time slots are not fixed, as in Synchronous TDM. Only those devices with data to send are assigned time slots. As a result, we may claim that an Asynchronous Time Division multiplexer only sends data from active workstations.
- The time slots are dynamically assigned to the devices using an asynchronous TDM method.
- The overall speed of the input lines in asynchronous TDM might be more than the channel capacity.
- Asynchronous Time Division multiplexor takes incoming data streams and generates a frame with no empty slots.
- Each slot in Asynchronous TDM has an address part that identifies the data source.
- The distinction between Asynchronous TDM and Synchronous TDM is that many slots in Synchronous TDM go unused, whereas slots in Asynchronous TDM are completely used. This results in shorter transmission times and more efficient channel usage.
- If there are n transmitting devices in Synchronous TDM, there are n time slots. If there are n transmitting devices in Asynchronous TDM, there are m time slots where m is less than n (mn).
- The number of slots in a frame is determined by a statistical examination of the number of input lines.
Advantages of Asynchronous TDM:
- There is the effective utilization of transmission capacity in this multiplexing.
Disadvantages:
- Frames of varying sizes are used in this Multiplexing.
- Because there are no distinct slots allotted to each user, the buffer address information is also required.
- This method does not guarantee a certain waiting time.
4. Code Division Multiplexing (CDM):
- Code Division Multiplexing allows several data signals to be delivered over a single frequency.
- FDM divides the frequency into smaller channels, but CDM allows users to use the entire bandwidth and broadcast signals at all times using a unique code. To disseminate signals, CDM employs orthogonal coding.
- Each station is given a unique code, known as a chip. Signals move independently with these codes over the whole bandwidth. The chip-code signal that the receiver must receive is known in advance.
Summary
In this article, we look at the concept of multiplexing, its history, the need for multiplexing, and also the different types of multiplexing. We also look at the different subtypes under Time Division Multiplexing, namely Synchronous and Asynchronous Time Division Multiplexing. We also take a look at the advantages and disadvantages of each of the multiplexing methods.