A developing country – India is the 5th largest economy in the world in terms of its nominal GDP. The Indian Financial System refers to all institutions, structures, and services that provide pecuniary facilities to the public.
It makes possible trade and transfers of funds in a secure manner. India, being a democracy has independent pillars of the financial system especially in the areas of banking, capital and stock markets, insurance, liabilities, claims, transactions, and investments.
It is important for wealth creation and the economic development of the country.
Characteristics, Importance, and Functions of the Indian Financial System
- Issuing and gathering of deposits.
- Supply of loans from the collected pool of money.
- The undertaking of financial transactions.
- Boosting the growth of stock markets and other financial markets.
- Setting up the legal commercial substructure.
- Provision of monetary and consultative services.
- Permits portfolio adaptation for existing assets.
- Allotment of chance and risk.
- It forges a connection between depositors and investors.
- Boosts depth and breadth of finances by increasing its horizon.
- It is responsible for capital creation.
- Adds time value to assets and money.
- To set up an entire payment structure and system.
- Allocate and dissipate the economic resources.
- To maintain the economic stability in the country and the markets.
- To create markets that can judge the investment performance.
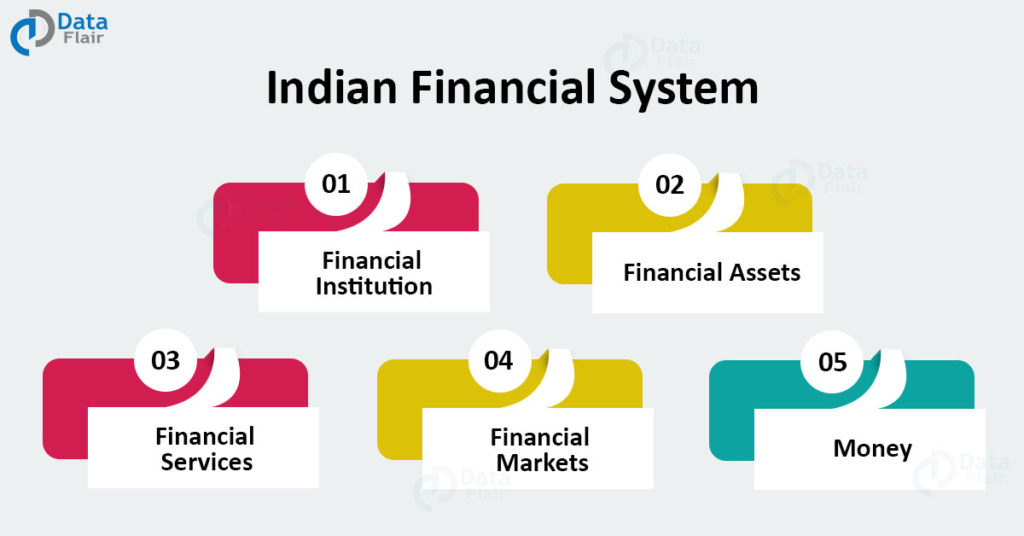
Components Of The Indian Financial System
It has 5 major components:
1. Financial Institution
- Their role is to mediate between the lender and the borrower.
- The lender’s savings are gathered through various commercial markets.
- These can turn risky financings into safe investments.
- A liability that is for a short duration can be turned into an investment for a longer duration.
- These can make comparable large deposits and loans with small deposits and loans due to uniform denominations.
- These provide a balance between the loan taker and the amount depositor.
Financial Institutions have 2 major types:
a. Banking Institutions or Depository Institutions
- Their role is to acquire money from the public.
- Interests are paid on these deposits made by the people.
- The lent money is then provided as loans to those who need it.
- Interests are charged on these loans given to those who require it.
- Examples include banks and other credit unions.
b. Non-banking Institutions or Non-depository Institutions
- Their role is to sell commercial and financial goods and products to those who visit them.
- These are based on offering insurance, mutual funds, brokerage deals, etc.
- Examples of these majorly include companies.
These further have 3 categories:
- Regulatory: Those managements and institutions which regulate and overlook the commercial and financial market. Example – RBI, IRDA, SEBI, etc.
- Intermediates: Those institutions which provide financial counseling and help by offering loans etc. Example – PNB, SBI, HDFC, BOB, Axis Bank.
- Non – Intermediates: These institutions help corporate visitors with their finances. Examples – NABARD, SIDBI, etc.
2. Financial Assets
- The objective of these is to provide convenient trade of securities in the commercial and financial market based on the requirements of those who seek credit.
- These are the goods or products which are sold in the financial market.
Financial Assets include:
- Call Money: Without any assurance, this is a loan lent for just a day which is repaid the next day.
- Notice Money: Without any assurance, this is a loan rent for more than a day but less than a duration of 14 days.
- Term Money: When the duration of the maturity of a particular amount deposited is more than 14 days.
- Treasury Bills: With the duration of maturity of less than a year, these belong to the government in the bond or debt security format. These are bought in the form of government T– Bills which are taken as loans from the government.
- Certificate of Deposit: This works on the format of electronic funds that remain deposited in a particular bank for a fixed period of time.
- Commercial Paper: Used by corporates, it is an instrument that is not secured even though for a short duration of debt.
3. Financial Services
- The major objective of these is to provide counseling to their visitors regarding the purchase or selling of a property, permitting transactions, deals, lending, and investments.
- These make sure the effectiveness of the investment and arrangement of the fund source too.
- These are usually taken up by asset and liability management companies.
Financial services also include in them:
- Banking Services: Functions performed by a bank such as the provision of loans, accepting debits, giving out credit or debit cards, account opening, granting checkbooks, etc are a part of these services.
- Insurance Services: These include services of offering insurance, selling policies, brokerage deals, etc.
- Investment Services: These services include overlooking and management of investment, assets, and deposits.
- Foreign Exchange Services: These include currency exchanges, foreign exchanges, and foreign fund transfers.
4. Financial Markets
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
The markets where trade and exchange of bonds, shares, money, investments, and assets take place between buyers and purchasers are these.
Financial markets have 4 major types:
a. Capital Market
- These deal with trades and transactions which take place in the market.
- These take place for a period of 1 year.
- These are of 3 major types:
- Corporate Securities Market
- Government Securities Market
- Long Term Loan Market
b. Money Market
- These are for short-duration investments.
- They are denominated by the government, banks, and other institutions.
- This market is based on wholesale debt having a low-risk factor with transparent instruments and formats used.
- It has 2 main types:
- Organized Money Market
- Unorganized Money Market
c. Foreign Exchange Market
- A highly developed market dealing with several currencies.
- It is responsible for the foreign transfer of funds.
- This takes place on the basis of foreign currency rates.
d. Credit Market
- This involves both short-duration loans and long-duration loans.
- It can be given to both individuals and organizations.
- These are granted by several banks, financial institutions, non – financial institutions, etc.
5. Money
It is an important medium of exchange that can be used to purchase goods and services. It can also act as a store of value. It is uniformly accepted everywhere.
It eases transactions especially impromptu daily purchases. It makes the goods and services easily exchangeable. It acts as a verifiable record in the socio-economic context.
Comparison between Money Market and Capital Market
| Money Market | Capital Market |
|
|
Conclusion
The above Indian financial system article increases awareness regarding the Indian Financial System. It helps prepare well for competitive exams.
This also encourages people to know more about the economic functioning of their country holds them able to make beneficial decisions regarding various investments.