In this Hadoop Yarn node manager tutorial, we will discuss node manager in Yarn, how it interact with the resource manager, how it allocates containers. We will also cover different Node manager components, how auxiliary services run in the node manager?
Introduction to Hadoop Yarn Node Manager
Conceptually, the NodeManager is more of a generic and efficient version of TaskTracker (of Hadoop1 architecture) which is more flexible than TaskTracker.
In contrast to fixed number of slots for map and reduce tasks in MRV1, the NodeManager of MRV2 has a number of dynamically created resource containers. There is no hard code split available into Map and Reduce slots as in MRV1.
The container refers to a collection of resources such as memory, CPU, disk and network IO. The number of containers on a node is the product of configuration parameter and the total amount of node resources. Node manager is the slave daemon of Yarn.
The Hadoop Yarn Node Manager is the per-machine/per-node framework agent who is responsible for containers, monitoring their resource usage and reporting the same to the ResourceManager.
Overseeing container’s lifecycle management, NodeManager also tracks the health of the node on which it is running, controls auxiliary services which different YARN applications may exploit at any point in time.
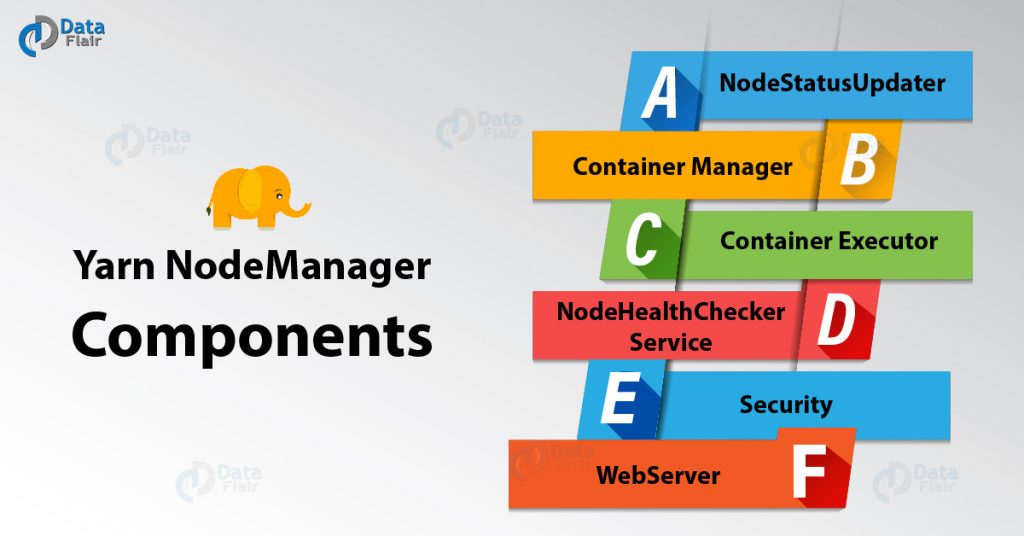
NodeManager can execute any computations that make sense to ApplicationMaster just by creating the container for each task.The above architecture diagram gives a detailed view of the NodeManager components.
The above architecture diagram gives a detailed view of the NodeManager components.
Yarn NodeManager Components
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
This section of Hadoop Yarn node manager tutorial will provide you a detailed description of yarn node manager components-
1. NodeStatusUpdater
On startup, this component registers with the ResourceManager(RM) and sends information about the resources available to every node. Subsequent NM-RM communication exchange updates on container statuses of every node like containers running on the node completed containers, etc.
In addition, the RM may signal the NodeStatusUpdater to potentially kill already running containers.
2. Container Manager
Being the core component of the NodeManager, shoulder the responsibilities of managing the containers running on each node with its sub-components, each of which performs a subset of the functionality that is needed to manage containers running on the node.
- RPC server- ContainerManager, that accepts requests from Application Masters (AMs) to start new containers, or to stop running ones. It works in association with ContainerTokenSecretManager to authorize all requests. All the operations performed on containers running on this node are written to an audit log which can be post-processed by security tools.
- ResourceLocalizationService- Responsible for securely downloading and organizing various file resources needed by containers. It tries its best to distribute the files across all the available disks. It also enforces access control restrictions of the downloaded files and puts appropriate usage limits on them.
- ContainersLauncher- Maintains a pool of threads to prepare and launch containers as quickly as possible. Also, cleans up the containers’ processes when such a request is sent by the RM or the ApplicationMasters (AMs).
- AuxServices- The NM provides a framework for extending its functionality by configuring auxiliary services. This allows per-node custom services that specific frameworks may require, and still sandbox them from the rest of the NM. These services have to be configured before NM starts. Auxiliary services are notified when an application’s first container starts on the node, and when the application is considered to be complete.
- ContainersMonitor- This component starts observing its resource utilization while the container is running. To enforce isolation and fair sharing of resources like memory, each container is allocated some amount of such a resource by the RM. The ContainersMonitor monitors each container’s usage continuously and if a container exceeds its allocation, it signals the container to be killed. This is done to prevent any runaway container from adversely affecting other well-behaved containers running on the same node.
- LogHandler- A pluggable component with the option of either keeping the containers’ logs on the local disks or zipping them together and uploading them onto a file-system.
3. Container Executor
Interacts with the underlying operating system to securely place files and directories needed by containers and subsequently to launch and clean up processes corresponding to containers in a secure manner.
4. NodeHealthChecker Service
The functionality of checking the health of the node by running a configured script regularly is the due responsibility of NodeHealthCheckerService. It also monitors the health of the disks specifically by creating temporary files on the disks every so often.
Any changes in the health of the system are notified to NodeStatusUpdater which in turn passes on the information to the RM.
5. Security
- ContainerTokenSecretManager: Examines incoming requests for containers to ensure that all the incoming requests are indeed properly authorized by the ResourceManager.
6. WebServer
Exposes the list of applications, container information running on the node at a given point of time, node-health related information and the logs produced by the containers.
In the case of MapReduce applications, the Map and Reduce tasks are executed inside the container. However, in between the Map and Reduce tasks (i.e, outside the containers) there is the ‘Shuffle and Sort’ phase.
The actions within this phase must be additionally specified to YARN as a NodeManager auxiliary service. Below is an illustration.
To summarize briefly, the key functionality of the NodeManager is to facilitate container launch on request from AM. Receiving the container launch request, the NM verifies this request, authorizes the user before resources assignment.