FREE Online Courses: Elevate Your Skills, Zero Cost Attached - Enroll Now!
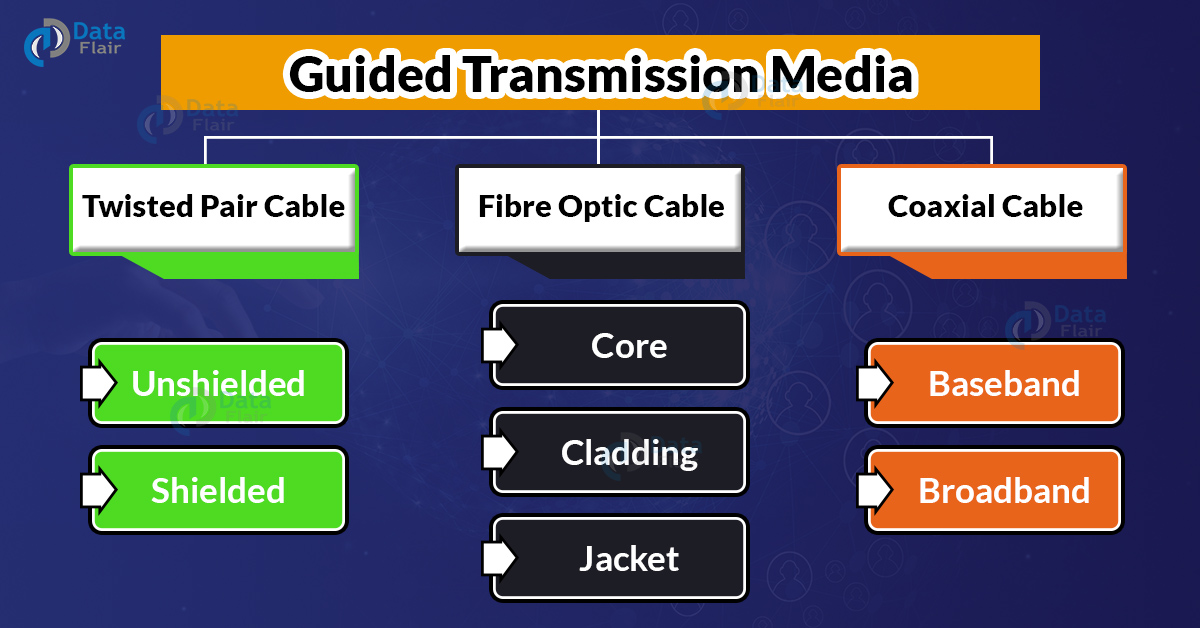
Twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable are examples of guided transmission media that offer a channel from one device to another. The physical boundaries of the medium direct and contain a signal flowing via any of these mediums.
Metallic (copper) conductors in twisted-pair and coaxial cable accept and convey signals in the form of electric current. Optical fibre is a type of cable that receives and transmits light signals.
Types of Guided Transmission Media:
1. Twisted Pair Cable:
This cable is the most often used and the least expensive. It is lightweight, inexpensive, and simple to install, and it supports a wide range of network types.
Twisted pairs are made up of 2 conductors (mostly copper), each with its own insulation, that are twisted together. One of these lines carries signals to the receiver, while the other serves merely as a ground reference. The difference between the two is used by the receiver to interpret signals.
In addition to the sender’s signal on one of the lines, interference may impact both wires and generate undesired signals. Because the two wires are in different positions relative to the noise sources, the effect of these undesirable signals is not the same in both wires if they are parallel. As a result, there is a difference at the receiver.
Types of Twisted Pair Cables:
a. Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable:
- When compared to Shielded Twisted Pair Cable, which comprises two conductors, generally copper, each with its own colour plastic insulator, Unshielded Twisted Pair is the most prevalent kind of cable used in telecommunication.
- UTP cables are made up of two or four pairs of twisted cables. RJ-11 connectors are used for two-pair cables, and RJ-45 connectors are used for four-pair cables.
Advantages of unshielded twisted pair cable:
- Simple to set up.
- Flexible
- Cheap
- Has a high speed capacity and a range of 100 metres.
- Higher grade UTP is utilised in LAN technologies such as Ethernet.
Disadvantages of unshielded twisted pair cable:
- Bandwidth is low when compared with the bandwidth of Coaxial Cable
- Provides less protection from interference.
b. Shielded twisted pair cable:
- Each pair of insulated conductors is encased in a metal foil or braided-mesh coating on this cable. Metal enclosure prevents electromagnetic noise from penetrating. Shielding also reduces crosstalk.
- This exhibits the same attenuation as an unshielded twisted pair. It outperforms unshielded and coaxial cable in terms of speed. It costs more than coaxial and unshielded twisted pair.
Advantages of shielded twisted pair cable:
- Installation is simple, and performance is sufficient.
- It may be used for both analogue and digital transmission.
- Increases the pace of signalling
- Unshielded twisted pair has a higher capacity than protected twisted pair.
- Crosstalk is eliminated.
Disadvantages of shielded twisted pair cable:
- Manufacturing is difficult.
- Heavy
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
Uses of Shielded Twisted Pair:
- Voice and data channels are provided in telephone lines. The telephone companies’ DSL lines, which enable high-data-rate connections, also make use of the high-bandwidth capabilities of unshielded twisted-pair cables.
- Twisted-pair cables are also used in Local Area Networks such as 10Base-T and 100Base-T.
2. Coaxial Cable:
- Coaxial is so named because it has two conductors that are parallel to each other. Copper is utilised as the centre conductor in this, which can be a solid wire or a normal wire. It is encircled by a PVC installation, a sheath, and an outside conductor made of metal foil, metal braid, or both.
- The outer copper wrapping serves as a noise barrier as well as the second conductor that completes the circuit. An insulating layer surrounds the outside conductor as well. The plastic cover on the outside covers the whole cable.
Types of Coaxial Cable:
a. Baseband Coaxial cable:
This is a coaxial cable with a resistance of 50 ohms () that is used for digital transmission. It is mostly used for LANs. Baseband transmits a single signal at a time at a high rate. The main disadvantage is that it requires amplification every 1000 feet.
b. Broadband Coaxial Cable:
This is accomplished through the use of analogue transmission over conventional cable television wiring. It sends several signals at the same time at various frequencies. When compared to Baseband Coaxial Cable, it covers a larger region.
Advantages of broadband coaxial cable:
- The bandwidth is really large.
- Long-distance telephone lines make use of this term.
- Digital signals are sent at a very high rate of 10Mbps.
- Significantly improved noise immunity
- Transmission of data with no distortion.
- Because they have greater insulation than twisted pair cable, they can traverse longer distances at higher speeds.
Disadvantages of broadband coaxial cable:
- A single cable failure may bring the entire network to a halt.
- When compared to twisted pair, it is more difficult to install and more costly.
- If the shield is not flawless, it might result in a grounded loop.
Uses of Coaxial Cable:
- Coaxial cable is used in analog telephone networks, with a single coaxial network capable of carrying 10,000 voice transmissions.
- These are also used in cable TV networks. Coaxial cable was utilised across the conventional cable TV network. Cable television employs RG-59 coaxial cable.
- In standard Ethernet LANs. Coaxial cable was selected for digital transmission in early Ethernet LANs due to its large bandwidth and, as a result, high data rate. 10Base-2, also known as Thin Ethernet, uses RG-58 coaxial cable with BNC connections to transport data at 10Mbps over a distance of 185 metres.
3. Fibre Optic Cable:
Fibre optic is a cable that contains optical fibres coated in plastic and is used to transmit data via light pulses.
The plastic covering shields the optical fibres from heat, cold, and electromagnetic interference caused by other types of wiring.
Fibre optics transmit data at a quicker rate than copper cables.
Parts of Fibre Optic Cable:
a. Core:
The optical fibre is made up of a thin strand of glass or plastic known as the core. A core is the portion of the fibre that transmits light. The larger the core area, the more light will be transferred into the fibre.
b. Cladding:
Cladding refers to the concentric layer of glass. The primary and foremost function of the cladding is to create a lower refractive index at the core interface, thereby causing reflection within the core and allowing light waves to pass through the fibre.
c. Jacket:
A jacket is a type of protective covering made of plastic. The primary function of a jacket is to retain fibre strength, absorb stress, and provide further fibre protection.
Advantages of fibre optic cable:
- Greater Bandwidth: When compared to copper, fibre optic cable delivers greater bandwidth. As a result, fibre optic cable can carry more data than copper wire.
- Faster data transmission: Fibre optic cable transmits data in the form of light. This enables the fibre optic cable to transport signals at a faster rate.
- Larger lengths: When compared to copper cable, fibre optic cable transports data across longer distances.
- Better reliability: Fiber optic cable is more dependable than copper cable since it is resistant to temperature fluctuations, which can create obstructions in copper cable communication.
- Thinner and more robust: Because fibre optic cable is thinner and lighter in weight, it can resist more draw pressure than copper wire.
Summary:
In this article, we looked at the various types of guided transmission media that are available, and also the advantages and disadvantages of each. We also covered the components within each cable, and also the use cases of these cables.