FREE Online Courses: Dive into Knowledge for Free. Learn More!
FTP is short form of File Transfer Protocol. It is a TCP/IP-based internet protocol that is used to transfer files from one host to another.
FTP is mostly used to transmit web page files from their developer to a computer that serves as a server for other computers on the internet. It is also used to download files from other servers to a PC.
Objectives of FTP:
- FTP allows for the exchange of files.
- It is employed to promote the usage of remote computers.
- It transports data in a more reliable and efficient manner.
Need for FTP:
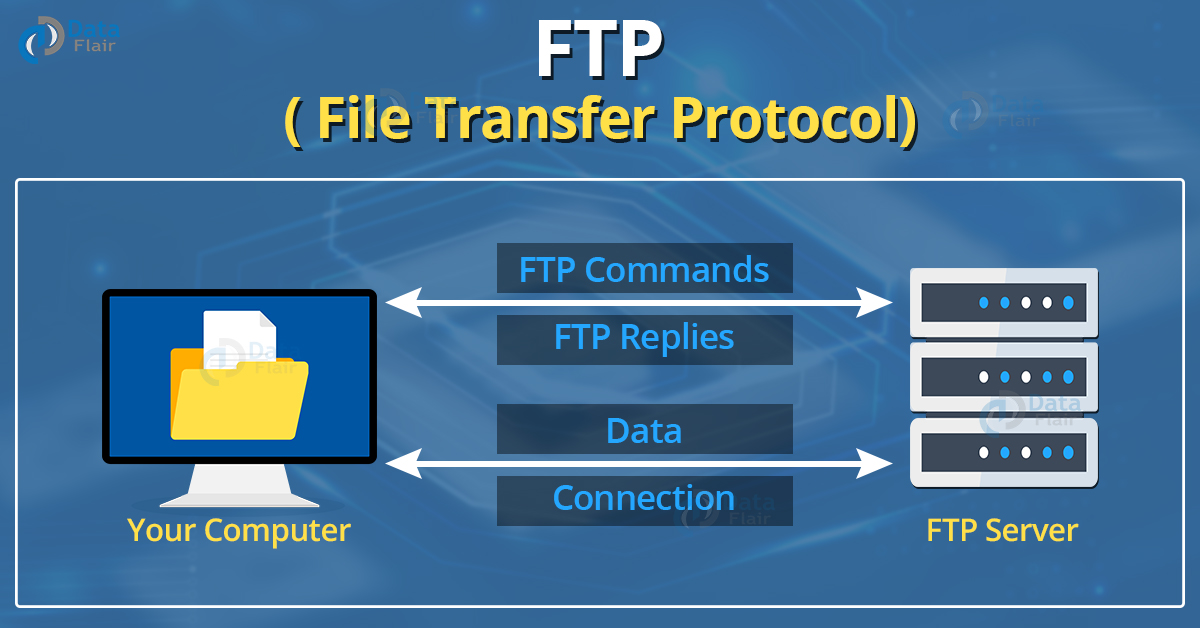
Although moving data from one system to another is easy and uncomplicated, it can occasionally cause issues. Two systems, for example, may have differing file conventions. Text and data may be represented differently in two systems. The directory structures of two systems may be different. The FTP protocol solves these issues by creating two connections between hosts. One link is utilised for data transport, while the other is used for control.
Types of Connections in FTP:
There are 2 types of connections within the File Transfer Protocol:
1. Control Connection:
FTP uses control connections to convey control information such as user identity, password, commands to alter the remote directory, commands to fetch and save files, and so on. The control connection is established on port 21.
2. Data Connection:
FTP uses a data connection to transfer the actual file. On port number 20, a data connection is established.
Because it utilises a separate control connection, FTP sends control information out-of-band. Some protocols send request and response header lines, as well as data, over the same TCP connection. As a result, they are said to convey control information in-band. HTTP and SMTP are two examples of such protocols.
Working of FTP:
The control connection connects the control processes, whereas the data connection connects the data transfer processes.
Technology is evolving rapidly!
Stay updated with DataFlair on WhatsApp!!
The control connection is kept open during the FTP interactive session, whereas the data connection is created and then closed for each file transmitted.
Simply said, when a user initiates an FTP connection, the control connection opens; while it is open, the data connection can be opened and closed numerous times if multiple files need to be transmitted.
Data Structures supported by FTP:
1. File Structure:
The file is essentially a continuous stream of bytes in the File data structure.
2. Record Structure:
The file is simply split into records in the Record data structure.
3. Page Structure:
The file is split into pages in the Page data structure, with each page having a page number and a page header. These pages can be saved and retrieved in either a random or sequential manner.
FTP Transmission Modes:
1. Stream Mode:
FTP’s default mode of transmission is Stream Mode. In this mode, the File is sent to TCP as a continuous stream of bytes.
There is no requirement for End-of-File if the data is merely in the form of a stream of bytes. Closing of the data connection by the sender is regarded as EOF or end-of-file. If the data is partitioned into records (the record structure), each record has an I-byte of EOR (end-of-record).
2. Block Mode:
Block mode is used to transfer data from FTP to TCP using data blocks. Each data block is preceded by three bytes of header, the first of which contains the block descriptor and the second and third bytes representing the block size.
3. Compressed Mode:
If the file to be transferred is particularly large, the data might be compressed in this mode. Normally, this technique is employed in run-length encoding. In the case of a text file, spaces/blanks are generally deleted. Null characters are compressed in the case of a binary file.
FTP Clients:
An FTP client is a software that uses a file transfer protocol to transmit data between two hosts on the internet.
It enables the user to connect to a remote server and upload or download files.
It comes with a series of instructions that we can use to connect to a host, transfer files between you and your host, and then disconnect.
The FTP software can also be found as a built-in component in a Web browser. This GUI-based FTP client simplifies file transfers and eliminates the need to memorise FTP commands.
FTP Commands:
- USER — This command delivers the user ID to the server.
- PASS — Used to send the user’s password to the server.
- CWD – Allows the user to operate with a different directory or dataset for file storage or retrieval without changing his login or accounting information.
- RMD – This command removes the directory specified in the pathname as a directory.
- MKD – This command creates a directory in the directory given by the pathname.
- PWD – This command returns the name of the current working directory in the response.
- RETR — This command instructs the remote host to establish a data connection and transfer the requested file across that connection.
- STOR – This command causes a file to be stored in the remote host’s current directory.
- LIST – Requests that a list of all the files in the directory be displayed.
- ABOR — This command instructs the server to cancel the preceding FTP service command and any associated data transfer.
- QUIT — This command terminates a USER and closes the control connection if no file transfer is in process.
FTP Replies:
- 200: OK.
- 530: You are not logged in.
- 331: User name is OK, but a password is required.
- 225: There is no data transfer in progress and the data connection is open.
- 221: Control link to the service is being closed.
- 551: The requested action was aborted because the page type was unknown.
- 502: Command has not been implemented.
- 503: Incorrect command sequence.
- 504: Command not available for that parameter.
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP):
It is suitable for basic file transfers, such as during startup.
It makes use of UDP as a transport layer protocol. The TFTP server must handle transmission failures (lost packets, checksum issues).
It only makes one connection through the well-known port 69.
TFTP employs a straightforward lock-step protocol (each data packet needs to be acknowledged). As a result, throughput is constrained.
Advantages of FTP:
- One of the most significant advantages of FTP is its speed. FTP is one of the quickest methods for transferring files from one computer to another.
- It is more efficient since we do not have to do all of the procedures to obtain the whole file.
- To gain access to the FTP server, we must enter the username and password. As a result, we may conclude that FTP is more secure.
- FTP allows us to transmit files back and forth.
Disadvantages of FTP:
- Passwords and file contents are delivered in clear text, allowing for unauthorised eavesdropping. As a result, attackers may be able to carry out a brute force attack by attempting to guess the FTP password.
- It is not compatible with all operating systems.
Summary:
In this article, we looked at the various aspects of the File Transfer Protocol (FTP). We looked at the various commands used in FTP and the various responses given by the FTP server. We also looked at the working of FPT, various modes of operation of FTP, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of FTP. Then we also explored a lesser-known version of FTP known as TFTP.